Catalyzing climate action
We recognize that climate resilience is vital to safeguarding public health and building societal trust. By integrating environmental sustainability into every facet of our worldwide operations, we proactively minimize emissions, conserve water, and reduce waste, ensuring our business remains future-ready and aligned with our long-term environmental objectives.
26%
Reduction in Absolute GHG Emissions (Scope 1 & 2) from the FY23 Baseline
39%
Share of Renewable Energy in our Operations in FY25
4
Years of Water Positivity in a Row
6
Manufacturing Plants are Zero- Liquid Discharge
Material Topics
Environmental Governance Practices
Our environmental governance is guided by our Environment, Health, Safety, and Sustainability (EHS&S) policy, which prioritizes resource optimization, reduction of pollution and waste material, conservation of energy and biodiversity, and water recycling.
All our facilities in India are certified to ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 standards, while our international sites undergo rigorous internal assessments aligned with stringent environmental management protocols. We continually assess our Environment, Health, Safety, and Sustainability (EHS&S) practices and performance covering all our global sites, ensuring detailed reporting on a quarterly basis to the Board. Our internal audits of the Environment Management System (EMS), along with periodic audits conducted by external certifying agencies covering energy, water, and waste reinforce this process. This is in adherence to regulatory compliance and provides a lever for continuous improvement.
EHS Audit
(Energy, Climate, Water, Wastewater and Waste Management)
Audits
Audits
To acknowledge contributions towards ESG targets, such as GHG emission reductions and water-saving initiatives, we have introduced the Environment, Health, and Safety Awards and Accolade System (EHSAAS) reward program for employees and contractors. These initiatives aim to improve our environmental performance and management systems.
Climate Action
As a responsible business, we acknowledge the potential impact of climate change on the environment, society, governance, and the economy.
In FY25, we conducted a comprehensive re-assessment of our global operations and value chain emissions to refine and optimize our decarbonization strategy, ensuring alignment with the Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi) standard. This study equipped us with a detailed roadmap for reduction of emissions.
To further this objective, we have undertaken various initiatives. We prioritized renewable energy procurement, encompassing captive solar and wind generation, and transitioned to briquette boiler operations using renewable fuel. We have been working closely with suppliers and logistics partners to drive the transition from air freight to ocean logistics. We are also exploring the introduction of green propellants in our inhalers, thereby reducing emissions throughout our value chain. Additionally, we established a dedicated Internal Carbon Pricing (ICP) mechanism as an integral part of our comprehensive climate strategy.
Lupin is committed to the Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi), aligned with the 1.5-degree reduction pathway.
- We aim to achieve an absolute reduction in Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions by 38% by FY30, with FY23 as the base year.
- We also target a reduction in Scope 3 emissions by 61.07% per unit value (economic intensity) by FY34, with FY24 as the base year.
Carbon Footprint
We have been working on reducing our carbon footprint through various initiatives, to mitigate the negative effects of climate change.
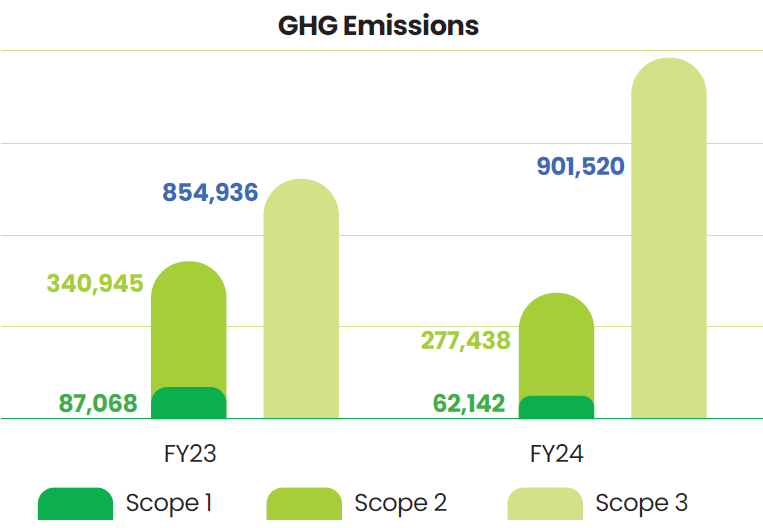
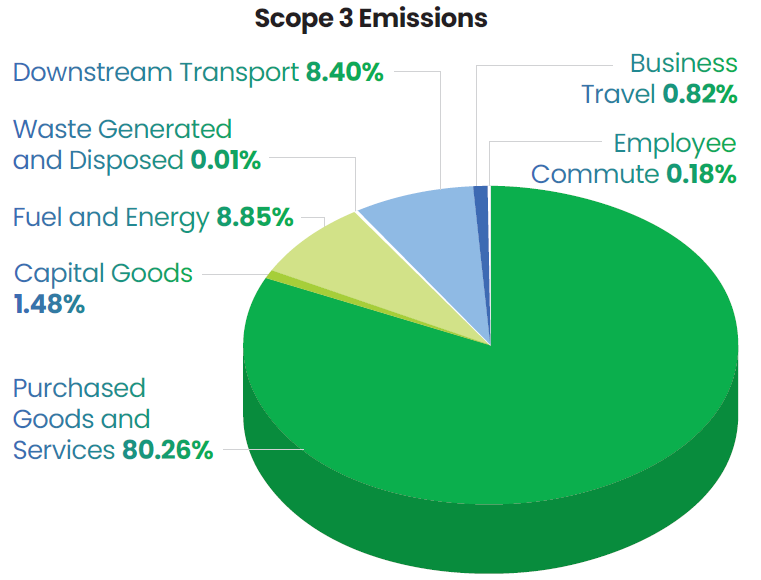
In FY25, we achieved a 26% reduction in our Scope 1 and Scope 2 carbon emissions, in comparison to 2023. Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions collectively account for 6% and 19% of our total global GHG footprint respectively, while 75% is emitted from our value chain (Scope 3).
A significant portion of our Scope 1 emissions originate from boilers used for producing steam. We have undertaken focused efforts to substitute oil-fuel boilers with biomass briquette boilers.
The majority of our Scope 2 indirect emissions are attributable to the electricity we procure. We have adopted renewable electricity across our operations to reduce our dependency on fossil fuelgenerated electricity.
Investments in renewable energy and the elimination of fossil fuels led to a 5% decline in Scope 1 emissions and a 10% drop in Scope 2 emissions, relative to FY24. Additionally, we achieved a 9% reduction in our Scope 3 emissions.
Lupin Healthcare, our subsidiary in the U.K., is committed to achieving net-zero Greenhouse Gas emissions by FY45. Some of their initiatives include:
- Completion of a GHG assessment
- Development of a Carbon Reduction Plan (CRP) which includes a clear roadmap toward achieving net zero
- Completion of the NHS Evergreen Sustainable Supplier Assessment to align with NHS sustainability goals
- Certification of the respiratory product portfolio as carbon neutral
- Working towards reformulation of products in the pMDI portfolio to incorporate a propellant with near-zero Global Warming Potential (GWP)
- Procurement of carbon credits to offset residual emission
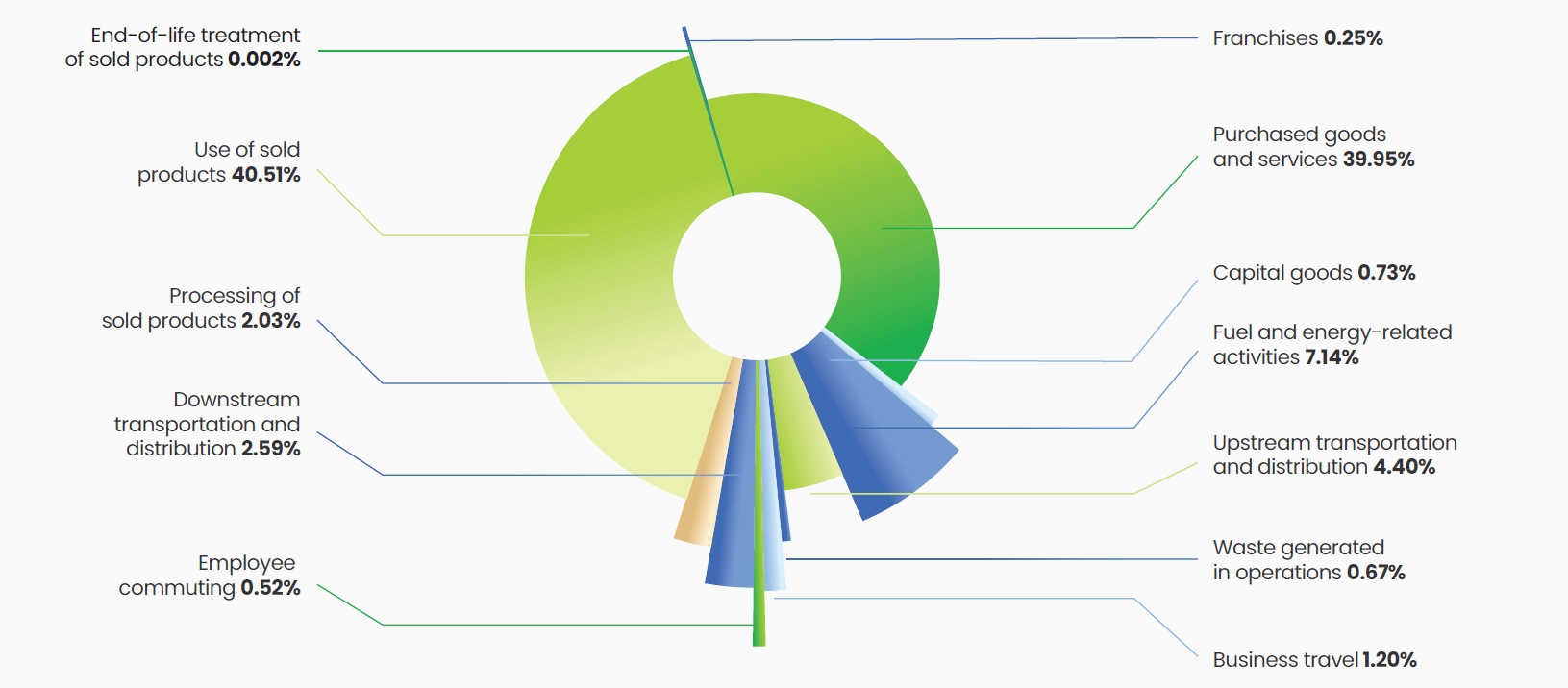
A significant part of our Scope 3 emissions stems from the use of purchased goods and services, as well as the use of sold products, collectively accounting for more than 80% of these emissions. With a view to minimize the emissions associated with the goods and services we procure, we are partnering with more than 300 suppliers. A crucial enabler for our emission reduction efforts is our collaboration with Honeywell. To mitigate emissions
from the use of our sold products, Lupin has teamed up with Honeywell to develop next-generation respiratory inhalers that utilize propellants with near-zero global warming potential. This intervention will mark a significant step in Lupin’s carbon reduction journey, given that our inhaler products account for ~35% of our Scope 3 emissions.
Energy Consumption and Reduction Measures
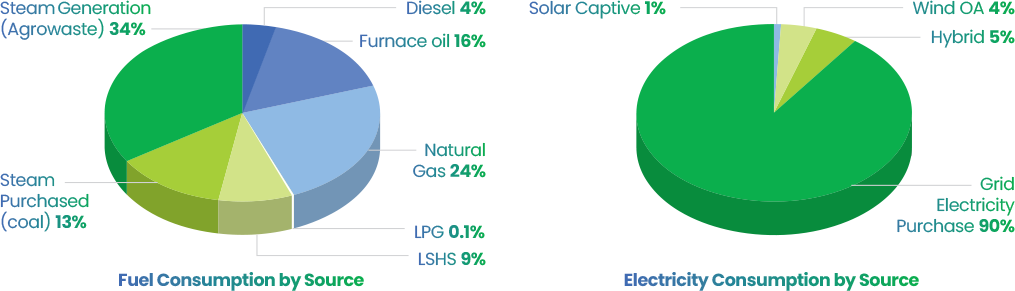
In FY25, our global energy consumption was 2,899,703 GJ, of which our 12 manufacturing operations in India were responsible for 97% and three international sites in U.S., Mexico and Brazil contributing to 3% of the total energy consumption.
Our primary energy requirements are met by grid-purchased electricity, biomass feedstock for boilers, fuel for fleet vehicles, and high-speed diesel for diesel generators (DG sets). We are actively reducing consumption and enhancing the efficiency across our manufacturing infrastructure, while steadily enhancing the share of renewable energy in our mix year-on-year.

FY25 Electricity Consumption by Source
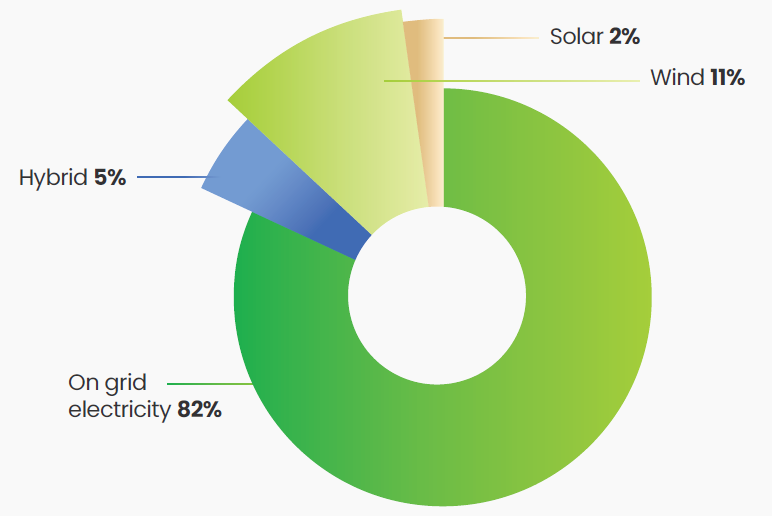
FY25 Fuel Consumption by Source

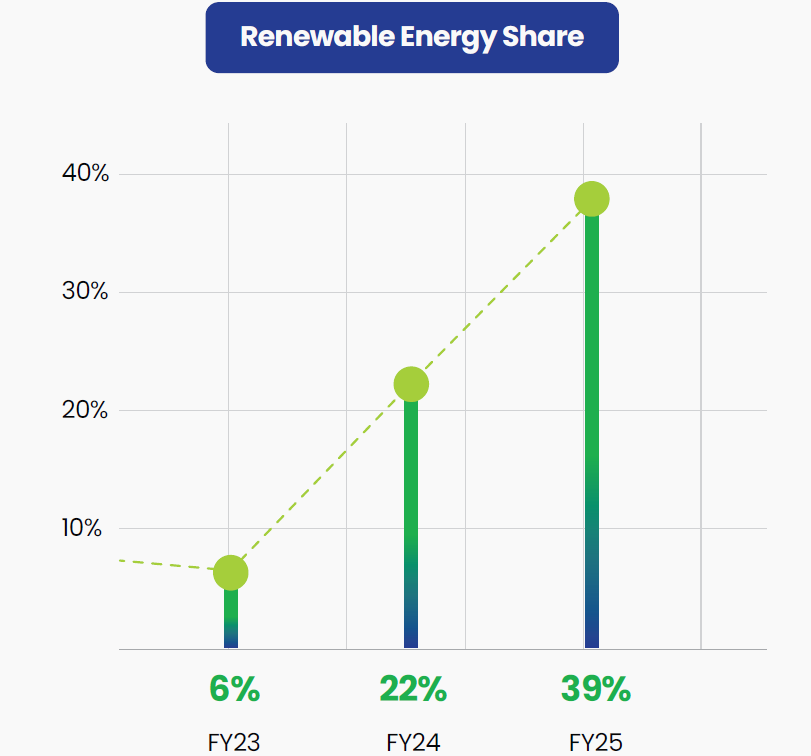
Share of renewable energy increased from 634,443 GJ in FY24 to 1,133,412 GJ in FY25, representing 39% of our total energy mix
Our energy management strategy includes several key components:
Energy Efficiency
We enhanced energy efficiency by implementing a range of measures, including upgrading to LED lighting, converting AC to DC motors, optimizing refrigeration and pumping systems, and installing heat pumps, boilers, and utility equipment. These initiatives have led to significant cost reductions and decreased CO 2 emissions.
We have reduced the consumption of approximately 31,200 MWh of energy across our manufacturing operations in FY25.
Renewable Energy Adoption
We have expanded our renewable electricity capacity, by over ten times, from 5 MW in 2021 to 58 MW by 2025 through the installation of rooftop solar panels and procurement of solar and wind energy. In FY25, 18% of the electricity consumed is from renewable sources.
Over the last three years, we have successfully transitioned fossil fuel boilers to biomass-based boilers in ten manufacturing units. Today, 78% of our primary energy is derived from renewable fuel.
Energy Savings League
We created a gamified program across our manufacturing units to engage employees in identifying energy-saving opportunities. Participants were rewarded for their innovative ideas, and the winning team received special recognition.
- Energy savings achieved at Pithampur Unit – 3,400 MWh/year
- Energy savings achieved at Tarapur Unit – 7,500 MWh/year
Energy Conservation Training
In FY25, we organized 21 training sessions at our manufacturing units to upskill our employees’ knowledge on the latest energy conservation technologies and practices.
Green Building: Our R&D facility, Lupin Research Park in Pune, has received LEED Platinum Certification for Operations and Maintenance from the U.S. Green Building Council, making Lupin one of the first Indian pharmaceutical companies to achieve this distinction. This is yet another reaffirmation of our commitment to sustainability and reinforces our leadership.
Climate Risk Assessment
With climate change being a major concern, we at Lupin meticulously monitor various external climatic factors to effectively manage associated risks. These risks pertain to the physical impact resulting from extreme weather and climatic events, as well as the outcomes related to adopting a low-carbon economy.
We have adopted the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) framework to identify and assess the potential risks associated with climate change within our global business operations, encompassing the entire value chain. We have established a robust governance process, supporting our strategy with targeted actions, and have integrated climate risk into our enterprise risk management framework. Furthermore, we have identified key metrics, set improvement targets, and assigned corresponding responsibilities and resources.
In accordance with the TCFD mandate and Carbon Disclosure Project, we undertook a climate risk assessment, that included scenario analysis, to evaluate the impact of climate change.
In FY25, we also undertook another detailed analysis of climaterelated risks and opportunities, the outcomes of which were compared with our TCFD findings. This was, reviewed by the Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility Committee, who observed them to be adequate for continuity.
Our TCFD report can be downloaded from this link: https://www.lupin.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/lupin-ir-2023-tcfd-v4.pdf
Physical Risk Assessment
A comprehensive physical risk assessment is essential to identify, evaluate, and manage potential hazards effectively. Over the last year, we assessed physical risks across 16 global sites, using the IPCC AR5 Risk Assessment Framework, as part of which we analyzed two climate scenarios: SSP 2 (middle of the road) and SSP 5 (fossil-fueled development). Extreme indicators including temperature, precipitation, cooling degree days, cyclones, and water stress were modelled for the periods 2020-2039 and 2040- 2059. We created a composite climate risk and vulnerability index, factoring in exposure, sensitivity, and adaptive capacity.

Key Potential Risks for Our Facilities
| High Temperature |
Vadodara Mumbai CSN Mandideep |
Rising temperature impacts the integrity of building structures Building’s energy usage will increase if extreme climatic conditions continue Wide temperature fluctuations to have an impact on staff’s comfort and productivity Heat waves are a primary cause of weather-related morbidity and mortality. It can have a direct impact on the health of the staff/ community in the vicinity |
|
| Cyclones |
Mumbai Visakhapatnam New Jersey, U.S. |
Disconnection/disruption of internet, telecommunication, or electricity services may lead to disruptions in business operations Infrastructure damage due to cyclones/winds, such as the collapse of the galvalume roofing system, failure of connections/ structures, progressive collapse of roof steel trusses, and breakage of window panes at plants and office sites |
|
| Sea Level Rise |
Mumbai Visakhapatnam |
Saltwater inundation |
|
| Dry Spell and Water Stress |
Mumbai Vadodara Indore Mandideep |
Dry spells may not directly impact the lab’s infrastructure but can result in water scarcity This could impact the site’s cooling systems, water requirement, and pools etc. Water scarcity can cause health and safety issues Limited water availability may also affect sanitation and hygiene |
|
Transition Risk Assessment
We performed a transition risk scenario analysis extending through 2050 to assess risks associated with anticipated changes in policies, current and emerging regulations, markets, and technologies due to climate change. In collaboration with an academic consortium comprising the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis, University of Maryland, Climate Analytics, and ETH Zurich, we employed Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) Scenarios. These scenarios investigate various transition pathways based on long-term temperature targets, net-zero objectives, short-term policies, overall policy coordination, and technology availability.
Water Stewardship
We at Lupin are focused on strengthening our water stewardship status. Our efforts are concentrated on optimizing water usage, minimizing water withdrawals, and enhancing water recovery. We are committed to prudent water usage in regions facing water scarcity.
The reduction and conservation of water consumption is a crucial element of our strategy, as it is essential for human health and the sustainable production of our medicines. This effort includes adhering to water-related regulations and enhancing the usage of recycled water obtained from effluent treatment and zero liquid discharge facility. We are also focused on optimizing freshwater use and enhancing water efficiency in our operations.
We take immense pride in having achieved a significant milestone of being “Water Positive” for four years in a row. This was made possible through multiple water reduction initiatives at our sites and focused efforts of water conservation at a community level.
Our dedication to responsible wastewater management is evident through our initiatives such as wastewater recycling and zero liquid discharge at six manufacturing sites. This ensures recycling and reuse of recovered water in utilities, thereby reinforcing our environmental sustainability commitment.
Our goal is to sustain our ‘Water Positive’ status year on year

Water Savings League
For the last two years, we have been conducting the ‘Water Savings League’ program, a gamified initiative under “Mission Jal Shakti,” at sites. This program included awareness camps and encouraged employees to share innovative water-saving ideas. As a result, numerous suggestions were implemented:
- Installing water flow meters at unmonitored usage points for accurate monitoring
- Using rainwater in the fire hydrant tank during the monsoon instead of fresh water
- Installing flow restrictors in taps to enhance water efficiency
- Removing redundant connections from the main water supply
Active employee participation in this program helped us reduce freshwater consumption by 1600 KL annually. Additionally, through this program, we trained 50+ employees on various water conservation methodologies as well as industry practices.
Reduction in Freshwater Consumption
Our CSN unit reduced effluent generation by 32% (approximately 40 KLD) and freshwater consumption by 32% (approximately 80 KLD) in FY25. Key initiatives identified and implemented were utilization of portable water RO reject for cooling tower makeup, RO reject reused for flushing and cleaning, and AHU condensate reused for cleaning.
We plan to join the Alliance for Water Stewardship (AWS) in the next fiscal year, to improve our water governance.
Waste Management and Driving Circularity
At Lupin, we are committed to minimizing our environmental footprint through a comprehensive and data-driven approach to waste management. We conduct regular waste audits across our operations to identify opportunities for improving waste performance and efficiency. Based on these insights, we implement targeted action plans aimed at reducing waste generation at the source. We have established quantified targets to minimize waste and continuously track our progress against these goals. Our investment in innovation and R&D enables us to explore new technologies and sustainable practices that further reduce waste.
To foster a culture of environmental responsibility, we provide waste reduction training to our employees across all levels. We have also integrated robust recycling programs to significantly reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills. Importantly, our waste diversion efforts are certified by an independent accredited body, ensuring transparency and accountability in our sustainability practices.
Guided by the 3R principle - Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle. We meticulously carry out an inventory of all our waste streams, including hazardous waste, non-hazardous waste, e-waste, and biomedical waste. We ensure responsible recycling or disposal through third-party service providers, in compliance with government requirements.
We have taken an ambitious target for achieving ‘Zero Waste to Landfill’ certification for 50% of our manufacturing plants in India by 2030 to improve waste circularity and reduce ecological impact.
To kick-start the journey of zero waste to landfill, we have institutionalized capacity building programs for our employees on waste management and circularity.
Hazardous Waste
At our sites, hazardous waste includes 3% plastic liners and drums, 20% chemical gypsum, 24% spent solvents, and 54% other hazardous materials designated for landfill, disposal, incineration without energy recovery, and co-processing.
In partnership with suppliers, we responsibly dispose both hazardous and non-hazardous waste. Over the last two years, we have repurposed 92% of disposed waste as alternative raw material or fuel for co-processing, reinforcing our commitment to sustainable hazardous waste management.
Non-Hazardous Waste
Our non-hazardous waste majorly comprises paper, metallic, non-metallic and food waste from our canteens. In the last two fiscal years, we have installed biomass composting systems at our manufacturing facilities, transforming biodegradable waste into high-quality organic manure which is used for plantation management within our premises. In the upcoming fiscal year, we have planned to install bio-composter units at two more manufacturing plants.
Other Waste
We responsibly dispose of all waste, including e-waste, plastic waste, and biomedical waste, in accordance with regulatory requirements. We adhere to the Central Pollution Control Board’s ‘Plastic Waste Management Rules,’ including Extended Producer Responsibility for plastic. We are 100% compliant to EPR regulation and have undertaken the collection and appropriate disposal/ recycling of 3041 MT of plastic waste.
Anti-Microbial Resistance
We assess the environmental impact of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, including water discharge, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. We routinely test treated water to ensure AMR PNEC (Predicted No-Effect Concentrations) values remain below quantifiable limits.
In FY25, two antibiotics (Ethambutol and Linezolid) were evaluated for Anti-Microbial Resistance (AMR) at one of the facility. The wastewater samples tested had limit of quantification well below PNEC limits for both the antibiotics, indicating safe manufacturing practices and effective wastewater management. An additional assessment of three more antibiotics is planned for the upcoming fiscal year.
Environmental Initiatives at MedQuimica Brazil
Our operations in Brazil continue to advance sustainability through focused environmental initiatives:
- Water: Reuse reverse osmosis discharge to reduce water consumption
- Air: Operate with low emissions and minimal incineration
- Energy: Purchase of renewable electricity
- Waste: 100% compliant waste disposal; over 50% recycled
- Effluent Treatment: Efficiency of 98% meeting local standards
Product Sustainability
At Lupin, we take utmost care to ensure that our new product development and existing product portfolio have a minimal environmental impact. We integrate sustainable practices into new product development, starting from design, keeping in mind the use phase of the product, choosing raw materials with lower environmental footprint, ensuring efficient manufacturing operations, streamlining our supply chain, and enabling appropriate end of life management.
Lupin utilizes Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) tools to assess and communicate the potential impact on human health and the environment of its products throughout their lifecycle. This year, guided by the ISO 14040 and ISO 14044 standards, we conducted LCA studies for 20 products.
Following up on the previous year, we have now completed LCA study of 30 major products.
This year’s LCA studies included both cradle-to-gate and cradle-to-grave assessments. Such assessments provided a holistic view of emissions from raw material production, to manufacturing and supply chain, to use phase, and finally to the disposal stage, as defined by our system boundary. We used the industry-leading SimaPro LCA software and EcoInvent database to model the environmental impacts of the chosen products.
The LCA report details the findings using eleven midpoint indicators, including Ecotoxicity and resource depletion indicators, to measure environmental impacts such as Climate Change/Global Warming Potential (GWP), Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP), human toxicity (cancer and non-cancer), Dust and Particulate Matter, Ionizing Radiation, Photochemical Ozone Creation Potential, Acidification Potential, Terrestrial, Freshwater, and Marine Eutrophication, Freshwater Ecotoxicity Potential, Land Use, Water Use, and Abiotic Depletion (Minerals and fossils) and Renewable Resource Depletion, Species richness.
| LCA Type | Products Covered in FY25 |
|---|---|
| Cradle-to-grave | Albuterol HFA, Salbair Transhaler HFA, and Budamate (Inhaler) |
| Cradle-to-gate | Tiotropium Bromide, Mirabegron, Luforbec, Rifapentine + (Inh), 4FDC, Novastat, Bupropion XL, Telista, Telekast, Ivabrad, Ondero, Levothyroxine Tabs, 2FDC, Doxy (Caps), Ethambutol, KIT A, and Rifampicin |
The findings of the LCA study highlighted the environmental impact of raw materials extraction and chemicals manufacturing (materials) accounts for more than 50% of the total environmental impact. Electricity and heating consumption add another 18% impact on total GWP of the assessed products.
The environmental hotspots identified in the study will be addressed through our decarbonization strategy and other process optimization plans. The LCA study will serve as a foundation to boost our development efforts encompassing green chemistry, and lead to the creation of environment-friendly pharmaceutical products.
Biodiversity
Preservation of biodiversity is crucial to the pharmaceutical industry, as it drives the discovery of nutraceuticals and other novel drugs by tapping nature’s rich reservoir of unique compounds and active ingredients.
Lupin acknowledges the critical impact of biodiversity on our business and the necessity for nature conservation. We conducted a thorough biodiversity assessment to evaluate risks related to our dependency and impact on biodiversity across our own operations and supply chain. We reaffirm our commitment to environmental sustainability by pledging elimination of deforestation and striving to achieve a net positive impact on biodiversity.
We prioritize our actions to minimize impact across land, freshwater, and atmosphere, while sustainably managing their dependencies. Our strategy is aligned with the recommendations of the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD), incorporating the L.E.A.P. (Locate, Evaluate, Assess, and Prepare) approach. This involves the identification and management of material nature-related Dependencies, Impacts, Risks, and Opportunities (DIRO).
As part of our commitment to environmental stewardship, biodiversity-related risks, both dependency and impact-driven, are systematically integrated into our company-wide, multidisciplinary enterprise risk management processes. We assess how our global operations depend on and affect biodiversity, and these insights inform our strategic planning and mitigation efforts. By embedding biodiversity considerations into our enterprise risk assessments, we aim to proactively manage potential disruptions and contribute to the preservation of natural ecosystems.
We embarked on comprehensive biodiversity risk assessments of our manufacturing sites aiming to cover 100% of our global sites by 2030. In 2024-25, we undertook assessments covering three of our key manufacturing facilities: Goa, Ankleshwar, and Nagpur.
Lupin is a member of the India Business & Biodiversity Initiative (IBBI). This membership signifies a commitment by participating businesses to align their operations with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (The Biodiversity Plan) and strive to operate in harmony with nature.
The findings of the biodiversity evaluations of the 3 manufacturing sites are:
No Lupin sites are located near any UNESCO World Heritage Site.
No Lupin sites are near any UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Reserves.
No Lupin sites are located near any Ramsar Site.
None of the faunal species at these plants feature in the IUCN RED list or have a protected status.
None of the three manufacturing plants are located within or near legally protected/biodiversity habitat areas.
The assessments involved detailed surveys of flora and fauna within a radius of 10 km of each site, utilizing the WWF Risk Filter and Encore tools to identify key risks and dependencies related to biodiversity. We identified potential vulnerabilities, including physical, political, and reputational risks. The significant physical risks noted were extreme heat, tropical cyclones, pollution, and disruptions in water supply. In the previous fiscal year, similar evaluations were conducted for three of Lupin’s largest sites: Mandideep, Pithampur, and Tarapur.
Our biodiversity risk assessment adopted TNFD’s LEAP assessment process, employing a combination of desk research and primary data collection methods. We conducted direct field observations, engaged internal and external stakeholders and collected remote sensing data to build a comprehensive picture. We also incorporated secondary data from environmental impact assessments, plant operation and production reports, and sustainability reports to ensure accuracy and depth.

| Lupin Sites | Simpson’s Diversity Index | |
|---|---|---|
| Tree Diversity Index | Tree Evenness Index | |
| Tarapur | 0.89 | 0.96 |
| Mandideep | 0.85 | 0.93 |
| Pithampur | 0.72 | 0.83 |
| Goa | 0.86 | 0.74 |
| Ankleshwar | 0.88 | 0.78 |
| Nagpur | 0.89 | 0.79 |
- Simpson’s Diversity Index = 1: Maximum diversity, perfect evenness.
- 0.7 ≤ Simpson’s Diversity Index < 0.9: High diversity, no single species dominating.
- Simpson’s Evenness Index = 1: perfect evenness, same abundance.
- Simpson’s Evenness Index close to 1 (>0.5) suggests high evenness, similar abundance levels.
Supply Chain Biodiversity Assessment
We have embarked on a journey to undertake a biodiversity assessment covering our entire supply chain, including both upstream and downstream stages. Through an independent third-party service provider, we are collaborating with critical suppliers to evaluate their biodiversity risks, impacts, and dependencies.
Supplier Biodiversity Scores (%)
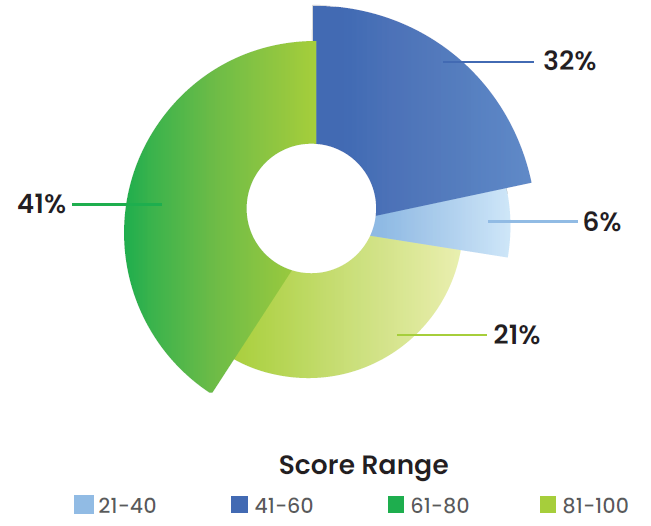
Additionally, through the Life Cycle Assessment study that we conducted with external consultants, we assessed the biodiversity impacts of our downstream activities.
Based on our assessment data, 79 suppliers have been assigned a Biodiversity Score for prioritization and engagement. These scores aim to evaluate the impact of suppliers on land use and biodiversity. The scores reflect the suppliers’ efforts towards no deforestation, biodiversity policy commitment, habitat destruction prevention, and pollution prevention initiatives. The objective is to measure biodiversity loss, which affects ecosystem services critical to human well-being. The outcomes of our biodiversity assessment are integrated into our company-wide risk management processes with appropriate mitigation measures.
Using methodologies from the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, we assessed the impact of our operations on local biodiversity. Based on this assessment, we developed two-level biodiversity management plans. Our goal is to achieve “no net loss” or, ideally, a “net-positive” impact on biodiversity and ecosystem services. We aim to prevent biodiversity loss, enhance ecological health, avoid habitat degradation, and meet sustainability goals, thereby fostering innovation and longevity in our industry.
Way Forward
We are leading the way as a low-impact pharmaceutical company, setting an example for the industry. Our commitment to science-based GHG emissions reduction targets, aligned with the SBTi, and our intention to join AWS and become a zerowaste- to-landfill company, reflect our dedication to minimizing the environmental impact of our operations.
Beyond mitigating operational impact, we are evaluating product carbon footprint and carrying out AMR analysis to gain deeper insights to optimize our operations. We are pivoting towards the adoption of low-GWP propellants in our inhalers portfolio to reduce customer-side emissions.
At Lupin, climate action is a priority and transcends regulatory compliance. We firmly believe in operating in harmony with nature and are committed to investing resources to significantly reduce our ecological footprint. As we move forward, we will intensify our focus on enhancing environmental performance across our global sites, ensuring that sustainability is embedded consistently throughout our global operations.

